What Is ADA compliance?

ADA compliance and web accessibility mean that people with disabilities can perceive, understand, navigate and interact with your website.
“Accessibility” describes the degree to which a product, device, service or facility is usable by people with all abilities and disabilities.
Why It Matters
People with disabilities and seniors are the two groups that benefit most from accessible technologies. However, implementing accessibility correctly will benefit everyone.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, 57 million
Americans have disabilities.
Approximately 30% of US households have a member with a disability.
Lastly, it’s the right thing to do!
Incorporating accessibility in your organization also has business incentives:
- SEO best practices align with accessibility best practices, which will increase traffic to your website.
- Increase consumer knowledge and use of products and services.
- Improve usability of the website.
- Avoid possible litigation risks and costs.
- Build business branding.
How It Helps
- Users with a vision impairment can access all financial services.
- Users who are hearing impaired can watch videos with closed captioning.
- All users can navigate through your website and gain access to information.
- Real life situations: Web Accessibility Perspectives.
Types Of Disabilities
Visual Disabilities
- No vision
- Low vision
- Little or no color perception
Auditory Disabilities
- No hearing
- Limited hearing
- Users with assisted listening devices
Speech Disabilities
- No speech
- Stuttering
Cognitive & Neurological Disabilities
- Limited cognitive, memory, language, & learning skills
- Susceptibility to seizures
Physical Disabilities
- Limited reach and strength
- Use of a prosthetic device
- Limited manual dexterity
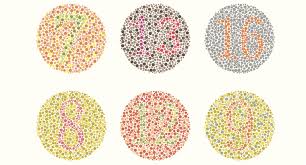
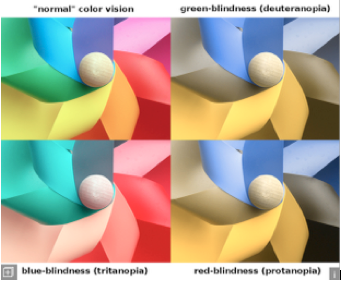
Examples of Color Blindness
Topics to Consider
- Site structure (titles, headings)
- Navigation (tab order)
- Text (contrast, size, color)
- Images (alt texts, contrast)
- Links (text, addresses, color)
- Forms (PDF accessibility)
Assistive Technologies
Definition: Product, device or equipment that is used to maintain, increase or improve the functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Examples
- Screen Reader (vision and cognitive)
- Refreshable Braille Display
(vision)
- Screen Magnifiers (low vision)
- Voice Recognition Software
(mobility impairment)
- Keyboard (most people with disabilities)
- Closed Captions (hearing and cognitive)
- Hearing Aids (hearing)
- Word Prediction Software
Where Are The Regulations Coming From?
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (as amended in 1998)
- Requires federal agencies to make their electronic and information technology accessible to people with disabilities.
- Applies to all federal agencies when they develop, procure, maintain, or use electronic and information technology.
- Federal Government may require a Voluntary Product Accessibility Template
(VPAT) to indicate a product’s conformance to Section 508 standards.
- On January 18, 2017, the Section 508 standards have been refreshed to account for new technology and align with WCAG guidelines.
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA)
Definition:
- The ADA is an “equal opportunity” law that gives civil rights protection for people with disabilities.
- Prohibits discrimination and guarantees equal opportunity for people with disabilities in public accommodations, employment, transportation, state and local government services and telecommunications.
Four Major Sections of the ADA:
- Title I – Employment
- Title II – Public Services
- Title III – Public Accommodations
- Title IV – Telecommunication
- Recent rulings have included websites as virtual accommodation to goods and services.
- Although not a formal guideline, the DOJ has required WCAG 2.0 Level AA as a base requirement for websites to meet ADA Title III requirements.
WCAG Guidelines
- The World Wide Web Consortium ( W3C) created the Web Accessibility Initiative
(WAI), which in turn created the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
- A globally recognized voluntary consensus standard for web content.
- WCAG content is organized into four main principles, with a total of 12 guidelines. Under each guideline is a series of success criteria, each of which are assigned a conformance level (Level A, AA, AAA).
Conformance Levels
Level A
For Level A conformance (the minimum level of conformance), the web page satisfies all the Level A Success Criteria, or a conforming alternate version is provided.
Level AA
For Level AA conformance, the web page satisfies all the Level A and Level AA Success
Criteria, or a Level AA conforming alternate version is provided.
Level AAA
For Level AAA conformance, the web page satisfies all the Level A, Level AA and Level
AAA Success Criteria, or a Level AAA conforming alternate version is provided.
- WAI-ARIA defines a way to make web content and web applications more accessible to people with disabilities.
- WAI- ARIA was created mainly to make web applications using advanced UI components (e.g. tree structure, tab, menu) that are not part of the HTML specification accessible to assistive technology users.
- WAI- ARIA specification provides attributes to convey accessibility information to assistive technologies
How Do I Make My Website Compliant?
Now that you understand what accessibility is and why it’s important, the next step is making your website meet WCAG 2.0 .
- Review your options
○ Free tools, such as WAVE , perform single page manual scans and are a great starting point.
○ Premiere tools provide an entire website audit, prioritize pages and issues, and train your staff how to make your website compliant.
○ Remediation companies will redesign your website for you ensuring ADA
compliance. This full service option can be costly.
- Perform an audit
○ Make sure to ask which standards they are using and how many issues they monitor for.
○ Free tools scan for around 90-100 WCAG 2.0 issues.
○ Premiere tools scan for around 115-175 WCAG 2.0 issues.
- Begin the project!





